- 12-02-2026
- Agile & Scrum
Mastering the Skills...
Mastering the Skills of a Product Owner: Essential Competencies for Ac...
![]() Get additional 5% off this Presidents’ Day!
Get additional 5% off this Presidents’ Day!
Enroll by 28th Feb
Promo Code NXT5

Introduction :-
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape characterized by Agile and lean methodologies, organizations are increasingly adopting the SAFe Framework to enhance business outcomes and boost operational efficiency. SAFe Practice Consultants are pivotal in facilitating the implementation of SAFe within organizations. This blog will delve into the roles and responsibilities of a SAFe Practice Consultant, the essential skills and qualifications required, and the expected salary range.
Who is a SAFe Practice Consultant (SPC)?
A SPC (SAFe Practice Consultant) is an Agile specialist primarily tasked with the adoption and implementation of the SAFe Methodology within an organization. These certified experts collaborate closely with leaders, teams, and stakeholders to ensure that the principles of SAFe are effectively applied throughout the organization.
Learn more about the SAFe Practice Consultant.
Why is the Role of SPC Important?
The SPC is crucial for organizations transitioning from traditional project management methods to Agile practices. The SAFe framework has emerged as a preferred choice for implementing Agile methodologies, necessitating a comprehensive understanding and skill set for effective execution. As organizations expand, they frequently encounter difficulties in scaling Agile practices across various teams and departments, which is where SPCs become essential.
Roles and Responsibilities of a SAFe Practice Consultant
The SPC role is multifaceted, requiring a profound grasp of Agile principles, leadership capabilities, and change management expertise. Below are some of the primary roles and responsibilities of SPCs:
An SPC collaborates with executives, managers, and teams to ensure that Agile transformation is in line with the organization's goals. They assist teams in adopting agile methodologies and implementing SAFe on a large scale, aiding in the definition and execution of strategic objectives, organizational frameworks, and key performance indicators.
Key Responsibilities:
Here are some of the key responsibilities:
2. Coaching and Mentoring
A crucial element of SPCs is coaching and mentoring Agile teams, scrum masters, product owners, and leaders to effectively apply SAFe principles. They guide teams through challenges and ensure ongoing improvement and evolution.
Key Responsibilities:
Some of the key responsibilities encompass:
3. Facilitating SAFe Implementation Workshops
An SPC is frequently responsible for facilitating and leading various SAFe training sessions, which may include Leading SAFe and SPC certification courses. These workshops are intended to help organizations develop a robust understanding of SAFe.
Key Responsibilities:
Here are some of the key responsibilities:
4. Supporting Continuous Improvement
The role of SPCs is crucial for advancing Agile practices beyond the initial implementation into continuously evolving and improved structures. These assessments, along with retrospective processes, provide organizations with vital feedback that guides process improvement.
Key Responsibilities:
Here are some of the key responsibilities:
5. Building Organizational Alignment
Implementing Agile transformations necessitates effective alignment among various teams and business units, as this is one of the greatest challenges. Through SPCs, organizations achieve consistent execution and comprehension of SAFe practices, resulting in continuous value delivery across the enterprise.
Key Responsibilities:
Here are some of the primary responsibilities:
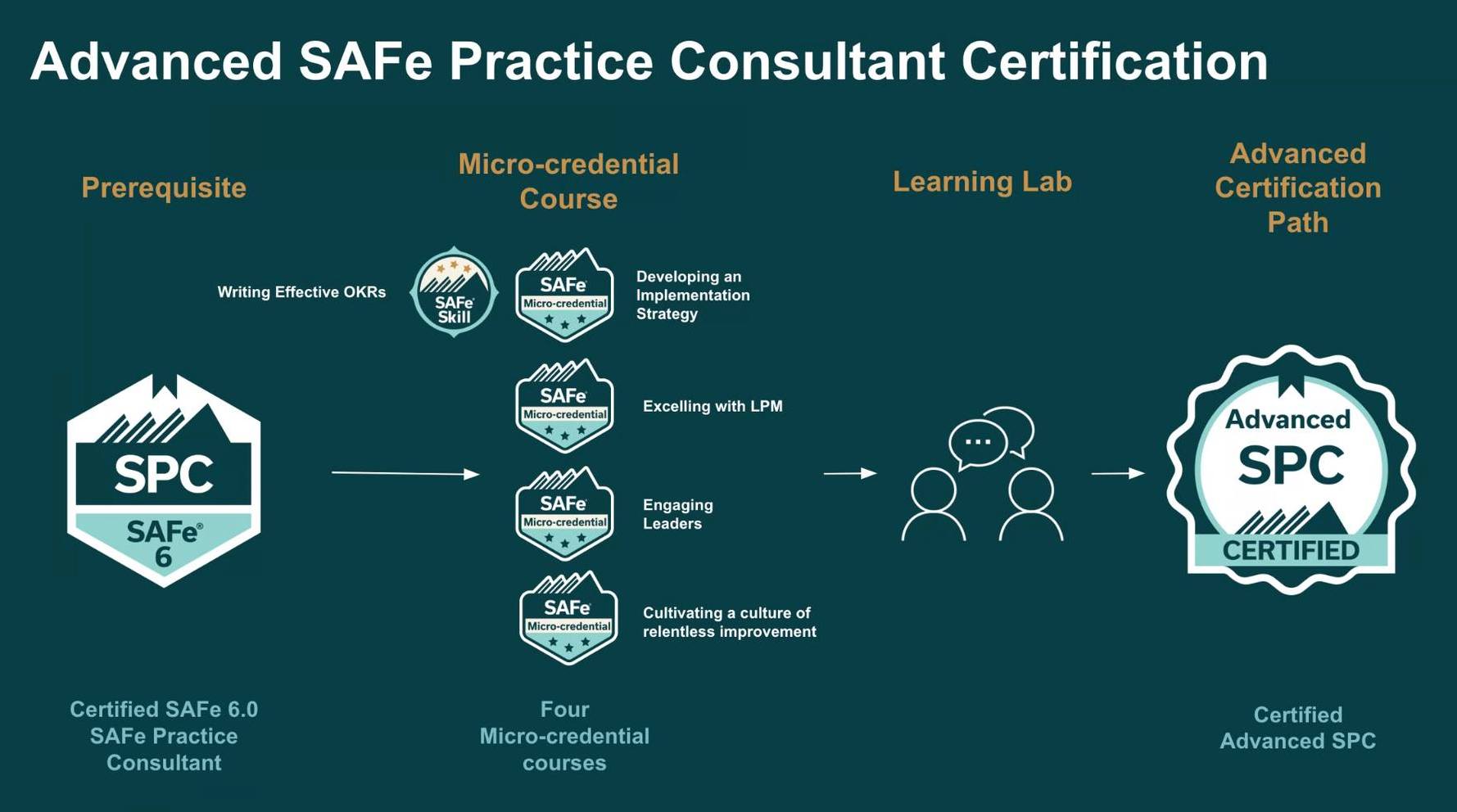
Check out the steps to become an SPC.
Skills and Qualifications Required for an SPC
Being an SPC involves more than just understanding the SAFe framework; it also necessitates strong leadership, coaching, and communication abilities. Below are the key skills required for an SPC:
| Skills | Description |
| Deep Knowledge of SAFe | SPCs should possess a comprehensive understanding of SAFe principles, roles, and practices. |
| Leadership Skills | SPCs should be capable of leading large organizations and instilling confidence in both leadership and teams. |
| Coaching and Mentoring | SPCs must be able to educate individuals and teams, assisting them in grasping Agile practices and principles. |
| Facilitation | Proficiency in leading workshops, training sessions, and discussions across various organizational levels. |
| Problem-Solving | Skill in identifying challenges and offering solutions that enhance Agile practices and team performance. |
| Excellent Communication | Ability to communicate clearly and effectively with executives, teams, and stakeholders to ensure alignment. |
| Analytical Skills | The capability to evaluate and measure the effectiveness of Agile processes and pinpoint areas for enhancement. |
The Influence of an SPC on an Organization
An SPC is crucial in assisting organizations to meet their Agile practice implementation objectives at various organizational levels. The following points highlight the primary benefits that an SPC brings to an organization:
1. Enhanced Agility
Organizations that embrace SAFe adoption alongside ongoing practice improvement experience greater responsiveness to market demands, resulting in quicker delivery of high-quality products.
2. Improved Collaboration
Through its SPC role, the organization links various teams, departments, and leadership, enabling them to work towards shared objectives in a coordinated manner.
3. Boosted Productivity and Quality
Organizations attain higher productivity levels through the effective application of SAFe practices, which empower teams to bring quality products to market more rapidly.
4. Longevity of Agile Practices
The adoption of Agile practices by SPCs fosters significant cultural transformation within the organization, ensuring that the change remains active and sustainable.
Conclusion
SAFe Practice Consultants (SPCs) are pivotal in guiding organizations to achieve successful SAFe implementations. SPCs undertake various responsibilities, including coaching teams, providing training, and conducting workshops, all while ensuring alignment across the enterprise. Organizations realize effective scalability of Agile practices through SPCs who are well-versed in SAFe principles and exhibit strong leadership skills to enhance collaboration, product quality, and delivery efficiency across the organization.
Join Centuera to discover SPC training and certification pathways that can assist you in implementing Agile practices within your organization. Centuera offers all the resources necessary for your success in SAFe transformation through its expert trainers.

Mastering the Skills of a Product Owner: Essential Competencies for Ac...
Mastering Product Owner Skills: Key Competencies for SuccessIn today’s...
What Is Capacity Planning? Definition, Top Methodologies, and MoreIn t...