- 20-06-2026
- Project Management
Project Management i...
us Project Management in the USA: Careers, Certifications & Indust...
![]() Get additional 5% off this Presidents’ Day!
Get additional 5% off this Presidents’ Day!
Enroll by 28th Feb
Promo Code NXT5


Project management refers to the process of directing and leading a team to accomplish specific objectives and deliverables while adhering to established constraints, including time, budget, and resources. It encompasses the planning, organization, and management of tasks and resources to guarantee that projects are finalized on schedule, within budget, and in alignment with the intended goals. Effective project management promotes efficiency and aids in achieving the overall objectives of the project while navigating challenges encountered along the way.
What Is Project Management?
Project Management involves the utilization of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to execute various tasks that fulfill project requirements, ultimately resulting in final deliverables within a defined timeframe and budget. There are six constraints in Project Management:
The scope defines a guaranteed set of deliverables, and the project is to be developed with this scope in consideration.
Time is one of the most crucial factors for stakeholders and a key indicator of project success. The duration required to complete the project must be estimated as accurately as possible.
Quality is an area that is frequently influenced by the other constraints. If time or cost is reduced, the quality of the project will be significantly impacted.
Cost is another critical element that must be taken into account, which includes an estimated total of labor costs, factory expenses, administration, software, and equipment.
The Project Manager must anticipate potential risks at every stage of the project. The risk component involves numerous what-if scenarios and the strategies to address those scenarios.
Every project necessitates a combination of resources essential for its success. Resources refer to the limitations that may impede the completion of a specific task, such as personnel, equipment, time, or other necessary supplies.
Now that we have a clear understanding of what project management entails, what exactly constitutes a project? Let’s delve deeper into this in the next section.
What is a Project?
The Project Management Institute (PMI) describes a project as a temporary effort aimed at producing a unique product, service, or outcome. The temporary aspect of projects signifies that each project has a clear start and finish. Initially, the project is defined, and as it moves forward, additional clarity is provided regarding its definition and scope. Projects go through various phases, from initiation to completion, which together form the project life cycle.
Our next subject in our exploration of project management is the project life cycle.
Project Life Cycle
Each stage of the project life cycle yields different results. The phases can be categorized as: Initiation, Planning, Execution, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closure.
Here is a more detailed breakdown:
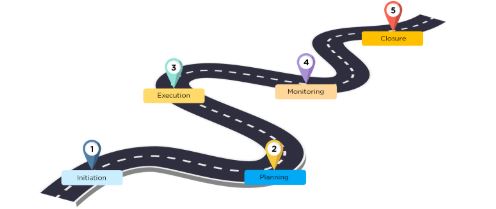
Initiation
The initiation phase is the first step in the project life cycle, which includes defining the project, identifying stakeholders, and assessing project feasibility.
Planning
The planning phase involves creating a project outline that encompasses costs, event sequencing, stakeholder communication, schedules, budget, and risk management.
Execution
The execution phase entails resource allocation, conducting meetings, providing updates, and delivering performance reports.
Monitoring and Controlling
Monitoring and controlling consist of tracking progress and comparing it to the plan, and it is crucial to perform quality control checks throughout the process.
Closure
The closure phase includes delivering the final product to the client and obtaining their feedback. It also requires evaluating the project to determine if everything proceeded as planned and discussing outcomes with stakeholders.
After the project life cycle, the next critical aspect that comes into play is the focus areas. Project managers must possess comprehensive knowledge of these focus areas in project management.
Let us examine some of the primary focus areas that will enhance our understanding of project management.
Key Focus Areas in Project Management
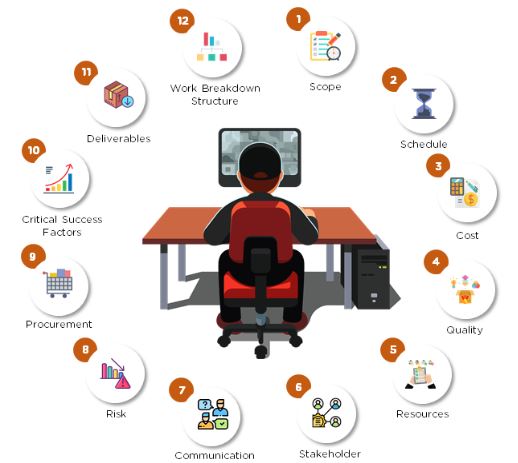
There are 12 primary focus areas that help us grasp the concept of project management:
Having navigated through the project lifecycle and key focus areas, you should now have a solid understanding of project management. Next, let’s explore the various job roles within this field.
Job Roles in Project Management
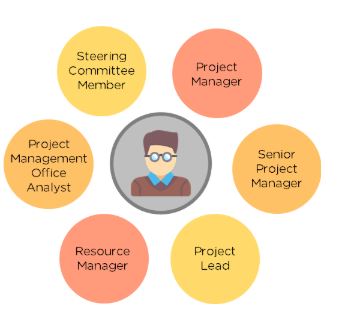
There are numerous job roles in Project Management. Some of these roles, along with their average salaries as reported by Glassdoor, include:
1. Project Manager
The Project Manager is responsible for steering the project according to the established plan and plays a pivotal role in all phases of project management. The Project Manager's duties encompass:
The success of a project is heavily influenced by the project manager, leading to a significant rise in the demand for project managers in the industry.
Salary trends for Project Managers are as follows:
US: $84,000/year
India: ₹15,00,000/year
2. Senior Project Manager
The Senior Project Manager oversees the entire Project Management plan; this position requires comprehensive knowledge of all project elements. The duties of the Senior Project Manager encompass:
The Senior Project Manager role is among the highest-paying positions in the industry, offering various allowances and bonuses.
The salary trends for a Senior Project Manager are as follows:
US: $104,496/year
India: ₹22,00,000/year
3. Project Lead
Project Leads are responsible for guiding team members throughout the project and providing them with all necessary information. The responsibilities of a Project Lead include:
Inspiring the team, addressing their needs, and being attentive to their feelings
The salary trends for a Project Lead are as follows:
US: $99,743/year
India: ₹18,00,000/year
4. Resource Manager
The Resource Manager is essential for providing the human resources necessary for project success. The responsibilities of a Resource Manager include:
The salary trends for a Resource Manager are as follows:
US: $80,562/year
India: ₹10,00,000/year
5. Project Management Office Analyst
Project Management Office Analyst operates within the PMO and primarily engages in data-driven tasks. The duties of the Project Management Office Analyst encompass:
The salary trends for a Project Management Office Analyst are as follows:
US: $137,746/yr
India: ₹575,000/yr
6. Steering Committee Member
Members of the Steering Committee do not directly engage in the project; instead, they support the Project Manager. The responsibilities of a Steering Committee Member include:
The salary trends for a Steering Committee Member are as follows:
US: $100,000/yr
India: ₹40,000/m
Now that we have a clear understanding of project management, let’s explore the certifications that can assist us in securing one of these project management positions.
Project Management Certifications
Certifications from the Project Management Institute (PMI) are highly valued in the field of project management, signifying the holder's dedication, knowledge, and proficiency in managing projects or programs. According to PMI, the costs, duration, structure, and prerequisites for each project management certification are outlined as follows:
1. Project Management Professional (PMP):
The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification stands as the most essential credential in project management, providing some of the highest-paying job prospects globally. Certified managers earn 20% more than the average salary.
OR
A high school diploma with 5 years of professional project management experience, 7500 hours of directing and leading projects, and 35 hours of project management education.
2. Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP):
The Agile Certified Practitioner certification signifies that an individual possesses the necessary experience and education to manage and lead agile projects. As organizations increasingly adopt agile methodologies, this certification has become one of the fastest-growing credentials worldwide.
3. Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM):
The CAPM is an entry-level certification initiated by the Project Management Institute (PMI), designed for individuals with limited project experience. It aims to showcase fundamental knowledge, terminology, and processes essential for effective project management.
4. Certified Scrum Master (CSM):
CSM is a foundational certification designed to assist professionals in starting their journey as Scrum practitioners. It is among the most desired certifications, as it allows individuals to achieve the title of Certified ScrumMaster, which is granted by Scrum Alliance.
5. Projects in Controlled Environments (PRINCE2):
This methodical approach to project management, established by the UK Government, is widely acknowledged and employed in the private sector, both in the UK and globally.
Conclusion
This wraps up our exploration of project management, including its key focus areas, job roles, and certifications. Certifications in Project Management, such as PMP, PRINCE2, and CSM, are recognized worldwide and can significantly enhance a project manager's salary. According to the PMI Global Survey, project managers holding a PMP certification earn 20 percent more than their non-certified counterparts.
The emergence of new technologies and the demand for quicker project processes are transforming how professionals manage projects, making it an exciting time for individuals to develop the latest project management skills.
PMP® and PMBOK® are registered trademarks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

us Project Management in the USA: Careers, Certifications & Indust...
The Leading 8 Project Management Certifications for 2026TL;DR: This ar...
The significance of a project director is well understood by all—the p...